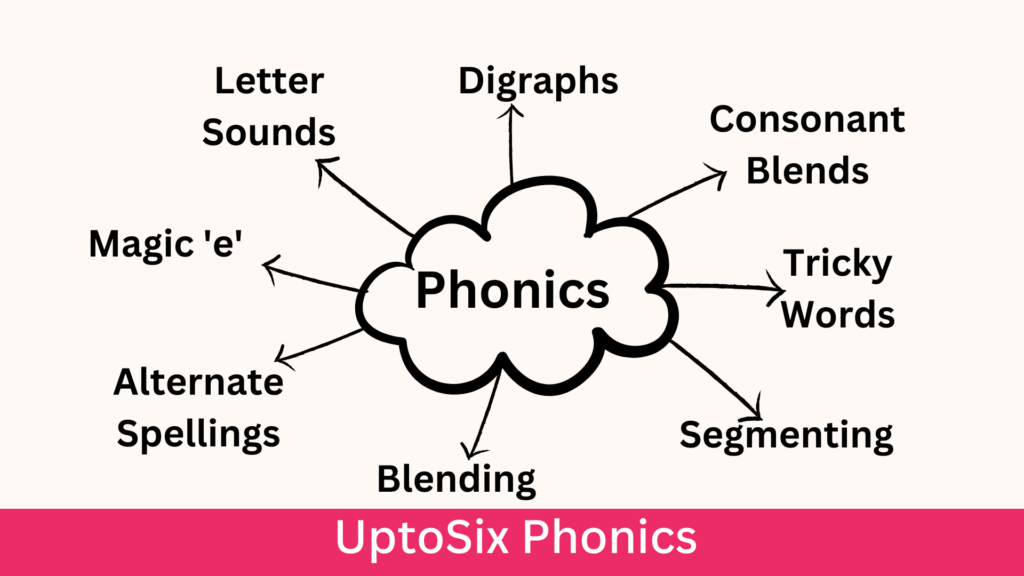
What is Phonics?
Introduction
Let us understand ‘What is Phonics’.
Phonics is a method of teaching reading and spelling. In this method, children learn the relationship between sounds (phonemes) and the letters or letter combinations (graphemes) that represent them in written language.
To read, children learn to blend the sounds.
Like, when the sounds /c/ – /a/ – /t/ are blended, children hear the word ‘cat’.
To spell, children learn to identify the individual sounds of a word and write the letters associated with those sounds.
This method is called segmenting.
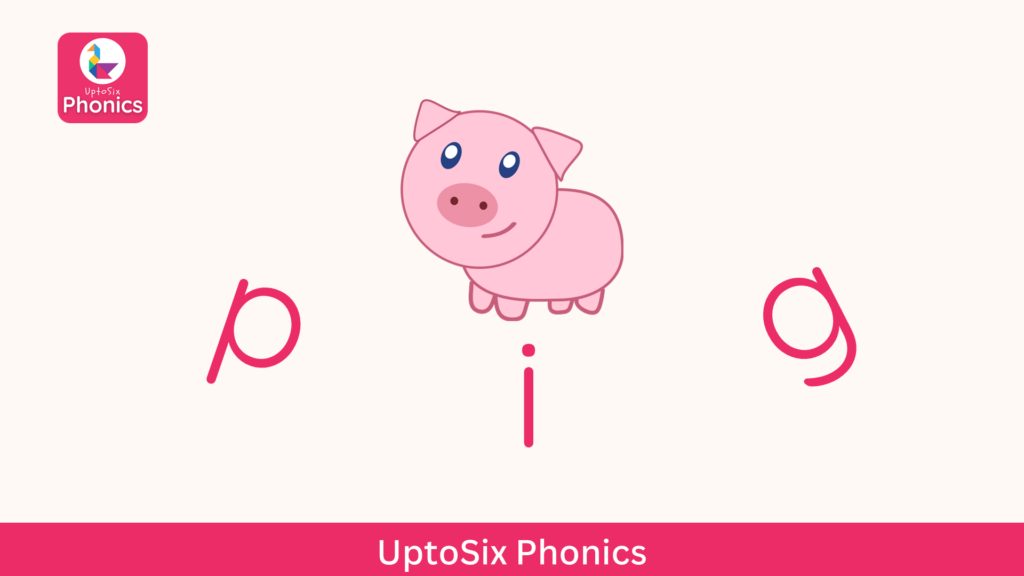
For example, to spell the word ‘pig’, children need to segment the words into the sounds /p/, /i/, and /g/ and write the letters associated with the sounds.
Why Phonics?
Phonics is essential for a child’s literacy development. The ability to connect letter symbols to their sounds is the foundation for learning to read and spell.
Like, the letter “Aa” makes the sound /a/, the letter “Ss” makes the sound /s/, and the letter “Cc” makes the sound /c/.
Children must learn that each letter has a sound and, each word is composed of sounds.
“Pig” is made up of three sounds: /p/, /i/, and /g/.
“Rain” has three sounds: /r/, /ai/, and /n/.
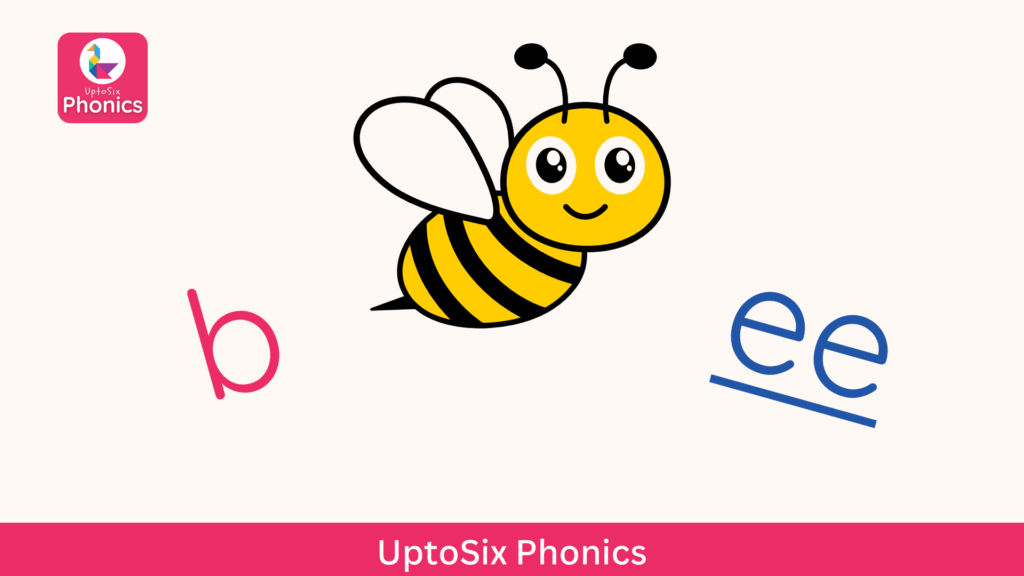
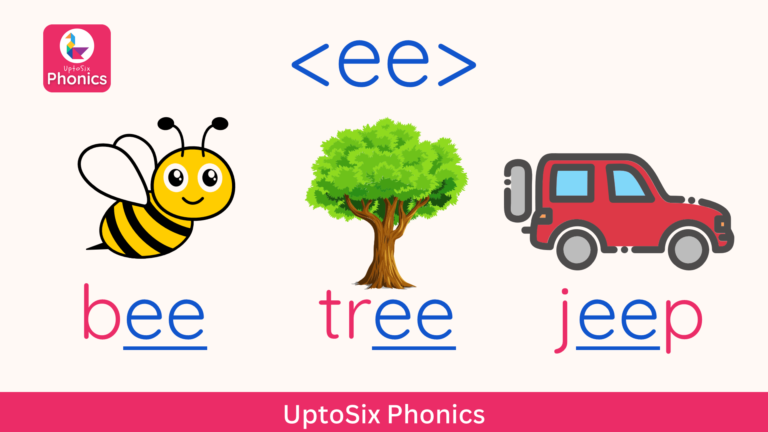
The word “bee” is composed of two sounds: /b/ and /ee/.
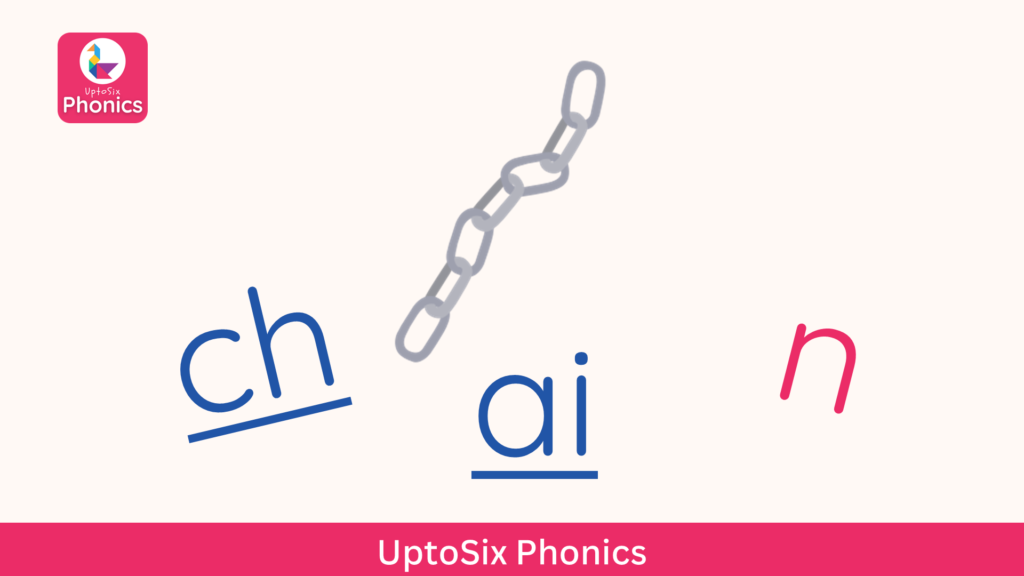
The word “chain” has three sounds: /ch/, /ai/, and /n/.
This is referred to as phonemic awareness.
Once children master the skill of blending sounds to read and segmenting a word into individual sounds to spell, they can read and spell almost any word. Isn’t it like a superpower? That’s why phonics is so important.

Though this might seem like a complex process, studies show early exposure to the teachings of phonics significantly impact a child’s reading and writing abilities.
So, engage your child in phonics activities as early as possible. It will help to build a solid foundation in reading and writing skills.
If you are wondering how to help your child with phonics learning because you do not have a very clear knowledge of phonics, please don’t worry. You can download the UpToSix phonics apps. They’re easy to use and will help you support your child’s learning without any fuss.
Download the UptoSix Phonics Apps
How Does Phonics Work?
Words are composed of sounds. There are 44 sounds in the English language, represented by 26 letters of the alphabet.
These sounds are called phonemes.
A grapheme is a written symbol that represents a sound or phoneme.
The relationship between the phoneme and grapheme is called phoneme-grapheme correspondence or letter sound relationship.


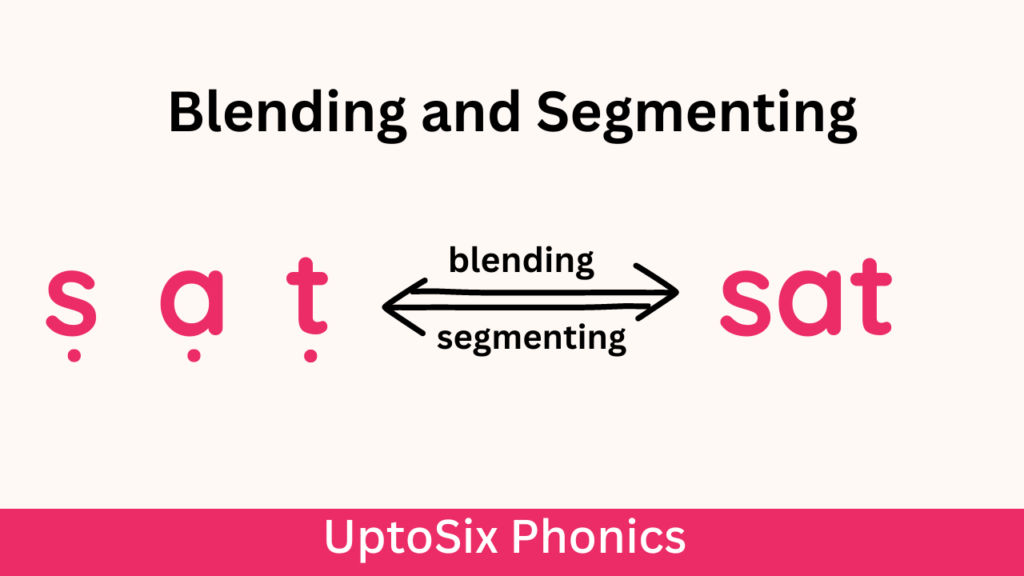
Blending
Blending is the skill of putting sounds together to read words.
To read, children look at the letters of a word from left to right, say the sounds, and blend the sounds to listen for the word. As /c-a-t/ => cat;
/h-e-n/ => hen
Or /f-i-sh/ => fish




Segmenting
Segmenting is the ability to identify the individual sounds in a word. The segmenting skill is used for spelling.
For example, to spell the word “dog,” one needs to hear the sounds in the word /d-o-g/ and write the letters associated with those sounds.
This skill is known as segmenting.
Children need a lot of practice to master the skills of blending and segmenting. It is like learning to ride a bicycle or to swim. Once they master the skills, they can decode and encode any unknown word.
For unlimited blending and segmenting skill practice, download the UptoSix Phonics apps.
Download the UptoSix Phonics Apps
Relationships between Blending and Segmenting
Blending and segmenting skills are just opposites of each other. To read or spell effectively, children should be fluent with the letter sounds, and letter-sound correspondence should be properly established.
Blending and segmenting skills should be practiced together. This helps children understand the mechanisms of reading and spelling. And children learn to blend and segment faster.
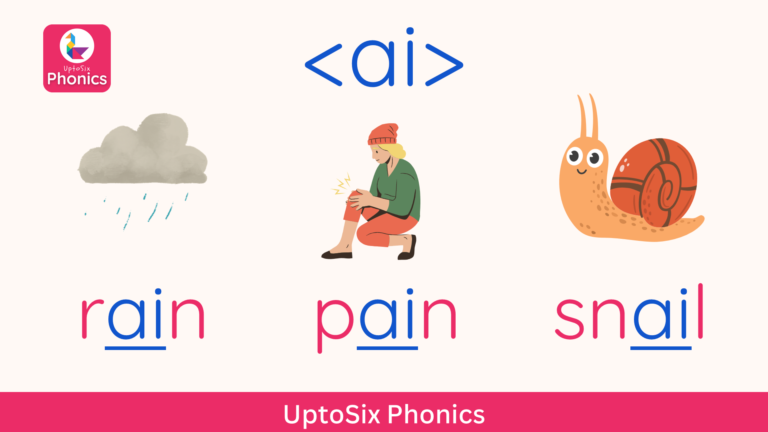
Digraphs
Digraphs are two letters and one sound.
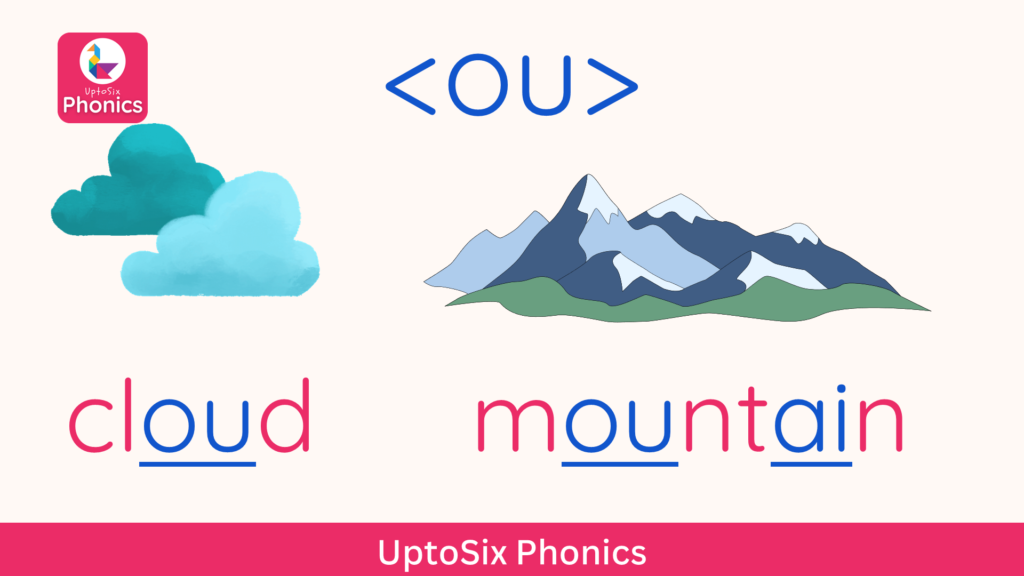

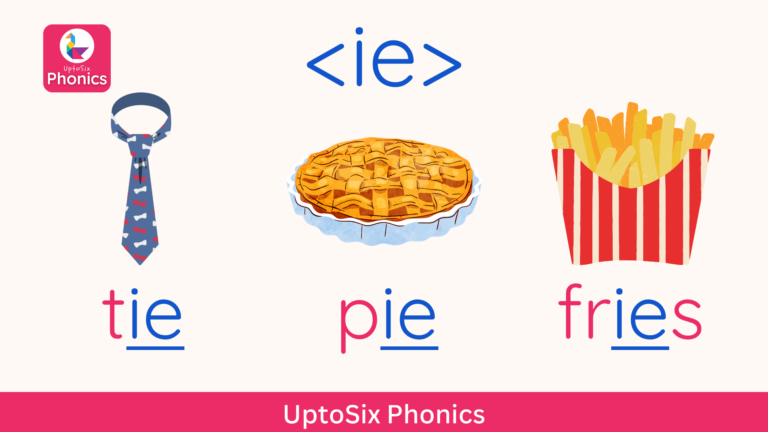
Notice there are two digraphs in “mountain”.
Consonant Blends
Words that begin with two or three consonants, such as train, brush, or street, can be difficult to blend for children.
If children say the sounds /t-r-ai-n/ or /s-t-r-ee–t/ it will be difficult for them to hear the word. Children will find it much easier to hear the word if they learn to blend the consonants and say them together: /tr-ai-n/ and /str-ee-t/.
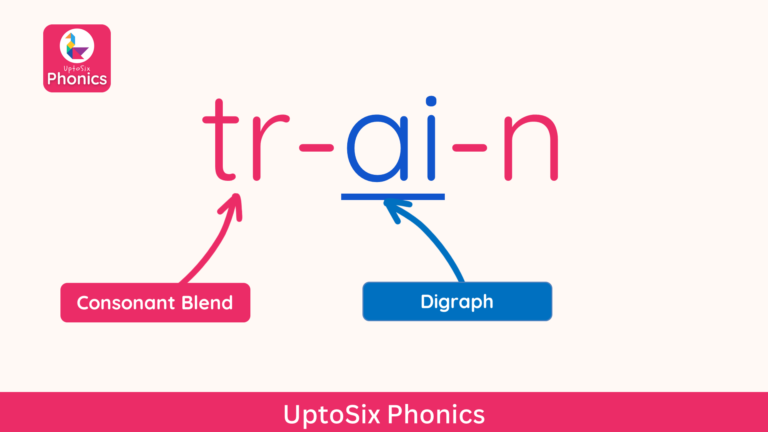
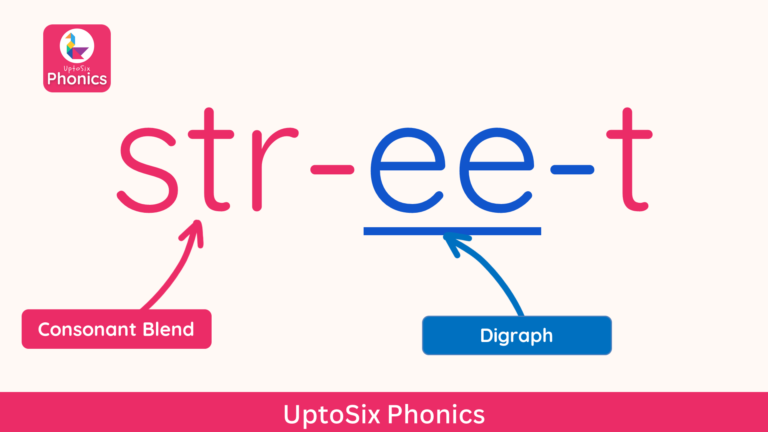
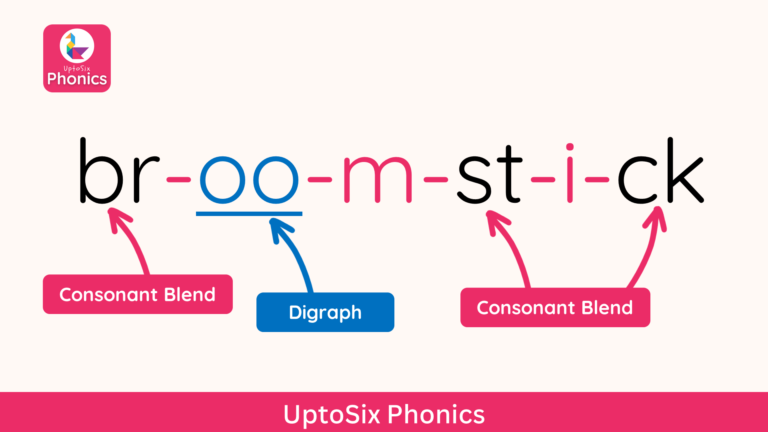
Consonant blends are a set of two to three consonant letters which retain their individual sounds when pronounced together. Consonant blends can come at the beginning, middle or end of a word.
Tricky Words/ Sight Words
Some words cannot be sounded out.
It doesn’t make sense if the sounds of the word ‘the’ are blended.
Words like these should be learned by sight.
‘By’, ‘my’, ‘he’, ‘she’ , ‘before’, ‘because’ are few examples of tricky words.
Magic 'e'
Magic ‘e’, makes a short vowel sound long.
Magic ‘e’, with its magical power, influences the vowel, which is one consonant away.
Magic ‘e’ taps the vowel with its magic wand and commands, “Vowel, forget your sound and say your name!” After performing the magic, Magic ‘e’ is too tired to make a sound, so he remains silent.




Two letters are needed to make the long vowel sounds in these words; however, these letters are not next to each other, as can be seen in cake, cube, pine, and hope. There is another letter, a consonant, in between the two vowels. Even so, the second vowel influences the first one and changes the sound from a short vowel to a long one. That is why ‘a_e’, ‘e_e’, ‘i_e’, ‘o_e’, and ‘u_e’ are referred to as split digraphs.
To learn about all these phonics concepts in detail, download the UptoSix Phonics PLUS App.
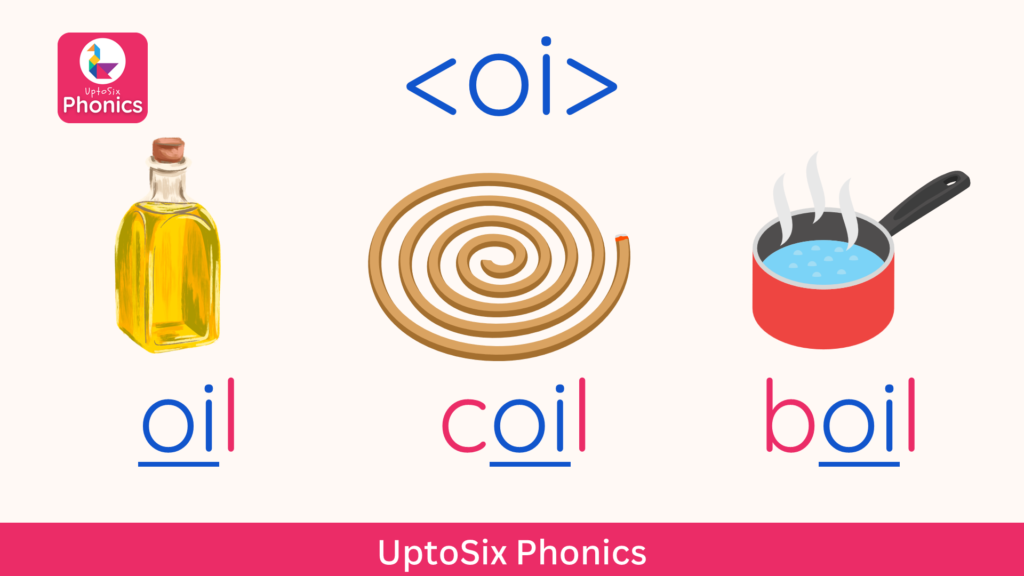
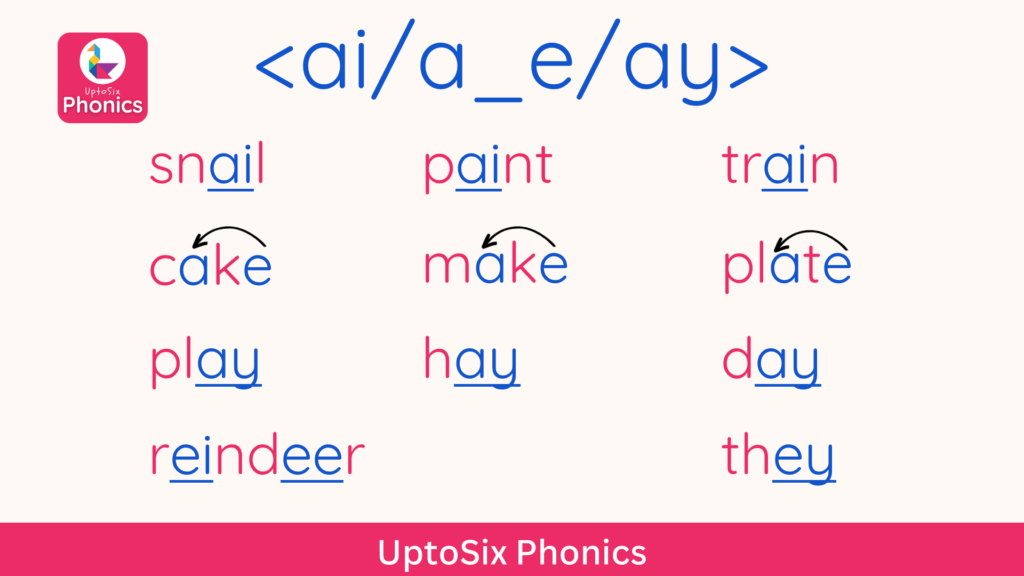
Alternate Spellings of Sounds
Some phonemes or sounds can be represented by different graphemes.
Let’s take the example of the sound <ay>.
In different words, the <ay> sound can be represented by any of these graphemes.
- <ai> as in rain, paint, brain
- <a_e> as in cake, made, plate
- <ay> as in day, hay, play
Conclusion
A solid foundation of reading and writing skills is essential for academic success. If a child struggles to read and write, he or she will struggle to learn any subject and will not be confident enough to express themselves through writing.
Phonics instruction gives children the ability to decode and encode words.
Starting with the basics, this strong foundation instills confidence in children and allows them to read and write thousands of words effortlessly.
Children gradually progress from reading words to phrases, then sentences, and finally books.
Phonics is a method to teach children reading and spelling. In this method, children learn the relationship between sounds (phonemes) and the letters or letter combinations (graphemes) that represent those sounds in written language. Children learn to blend the sounds to read. To spell, children segment a word into individual sounds.
Teaching phonics involves a systematic approach that gradually introduces students to letter-sound relationships and helps them develop the skills needed to decode words. Here’s a general outline of how phonics is typically taught:
- Sound Introduction
- Playing games helps develop listening skills.
- Blending to read
- Segmenting to spell
- Sight words or tricky words:
- Practice and Application: Provide plenty of opportunities for students to practice phonics skills through reading, writing, and word-building activities.
By following these steps and providing ongoing support and practice, educators can help students develop strong phonics skills essential for reading and spelling success.
If parents and teachers have a proper understanding of the phonics concepts, then teaching children to read and write with phonics is very easy, and phonics is very effective too.
If you are new to phonics, you can download the UptoSix Phonics App (for foundational phonics skills) and the UptoSix Phonics PLUS App (for advanced phonics skills) and easily help your child or student learn to read and spell with phonics.
The apps are available on the Google Play Store and App Store





